- Primary sources are original materials created during the time under study.
- Secondary sources analyze, interpret, or summarize primary sources.
- Examples of primary sources include research papers, original documents, and firsthand accounts.
- Examples of secondary sources include articles, books, and reviews that discuss primary sources.

Understanding Primary and Secondary Sources in Research
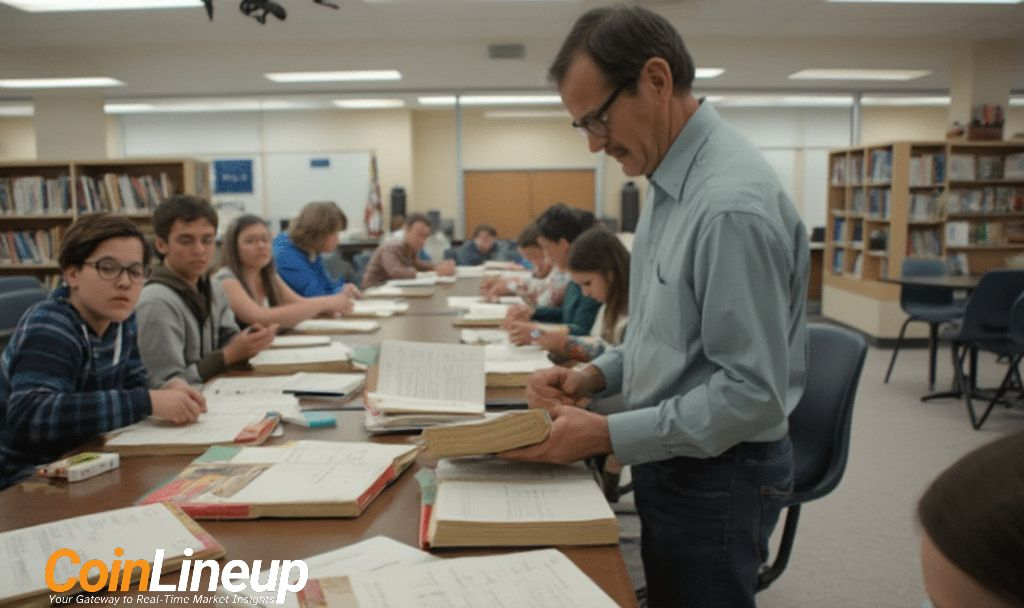
In the realm of research, distinguishing between primary and secondary sources is crucial for accurate analysis and interpretation. Primary sources provide direct or firsthand evidence about an event, object, person, or work of art, while secondary sources offer analysis or commentary on those primary sources.
Primary Sources
Primary sources are original materials that have not been altered or distorted in any way. They are created at the time when the events occurred or were created by individuals who experienced those events. Examples include:
- The Effectiveness of CEO Leadership Styles in the Technology Industry
- Tri-Start Matrix Book
- PM Archive – Firmenpresse
Secondary Sources
Secondary sources, on the other hand, analyze, interpret, or summarize primary sources. They provide context and understanding of the primary data. Examples include:
- Where’d All The Time Go? Scott McMicken on Dr. Dog’s Last Tour
- Wordlist Download
- 500K Wordlist
- Faculty & Staff – Mike Curb Arts, Media, and Communication
- TweetSafe Notebook Checkpoint
Understanding the distinction between these two types of sources is essential for researchers, students, and anyone looking to gain a deeper understanding of a subject.